07springboot指标监控
8、指标监控
1.SpringBoot Actuator与Endpoint
未来每一个微服务在云上部署以后,我们都需要对其进行监控、追踪、审计、控制等。SpringBoot就抽取了Actuator场景,使得我们每个微服务快速引用即可获得生产级别的应用监控、审计等功能。
官方文档 - Spring Boot Actuator: Production-ready Features
1.x与2.x的不同:
- SpringBoot Actuator 1.x
- 支持SpringMVC
- 基于继承方式进行扩展
- 层级Metrics配置
- 自定义Metrics收集
- 默认较少的安全策略
- SpringBoot Actuator 2.x
- 支持SpringMVC、JAX-RS以及Webflux
- 注解驱动进行扩展
- 层级&名称空间Metrics
- 底层使用MicroMeter,强大、便捷默认丰富的安全策略

如何使用
- 添加依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
- 访问
http://localhost:8080/actuator/**。 - 暴露所有监控信息为HTTP。
1 | management: |
-
测试例子
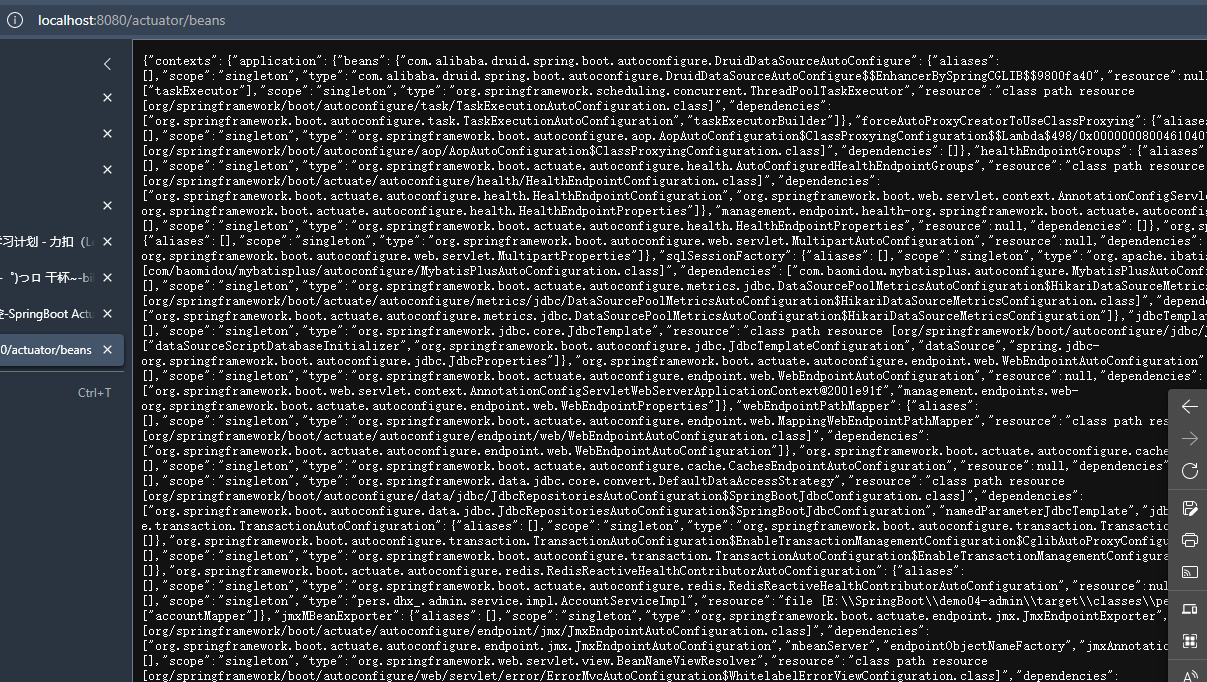
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/configprops
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/jvm.gc.pause
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/endpointName/detailPath
actuator
英 [ˈæktjʊeɪtə] 美 [ˈæktjuˌeɪtər]
n. 致动(促动,激励,调节)器;传动(装置,机构);拖动装置;马达;操作机构;执行机构(元件);(电磁铁)螺线管;操纵装置(阀门);调速控制器;往复运动油(气)缸;作动筒
metric
英 [ˈmetrɪk] 美 [ˈmetrɪk]
adj. 米制的;公制的;按公制制作的;用公制测量的
n. 度量标准;[数学]度量;诗体;韵文;诗韵
2.常使用的端点及开启与禁用
常使用的端点
| ID | 描述 |
|---|---|
auditevents |
暴露当前应用程序的审核事件信息。需要一个AuditEventRepository组件。 |
beans |
显示应用程序中所有Spring Bean的完整列表。 |
caches |
暴露可用的缓存。 |
conditions |
显示自动配置的所有条件信息,包括匹配或不匹配的原因。 |
configprops |
显示所有@ConfigurationProperties。 |
env |
暴露Spring的属性ConfigurableEnvironment |
flyway |
显示已应用的所有Flyway数据库迁移。 需要一个或多个Flyway组件。 |
health |
显示应用程序运行状况信息。 |
httptrace |
显示HTTP跟踪信息(默认情况下,最近100个HTTP请求-响应)。需要一个HttpTraceRepository组件。 |
info |
显示应用程序信息。 |
integrationgraph |
显示Spring integrationgraph 。需要依赖spring-integration-core。 |
loggers |
显示和修改应用程序中日志的配置。 |
liquibase |
显示已应用的所有Liquibase数据库迁移。需要一个或多个Liquibase组件。 |
metrics |
显示当前应用程序的“指标”信息。 |
mappings |
显示所有@RequestMapping路径列表。 |
scheduledtasks |
显示应用程序中的计划任务。 |
sessions |
允许从Spring Session支持的会话存储中检索和删除用户会话。需要使用Spring Session的基于Servlet的Web应用程序。 |
shutdown |
使应用程序正常关闭。默认禁用。 |
startup |
显示由ApplicationStartup收集的启动步骤数据。需要使用SpringApplication进行配置BufferingApplicationStartup。 |
threaddump |
执行线程转储。 |
如果您的应用程序是Web应用程序(Spring MVC,Spring WebFlux或Jersey),则可以使用以下附加端点:
| ID | 描述 |
|---|---|
heapdump |
返回hprof堆转储文件。 |
jolokia |
通过HTTP暴露JMX bean(需要引入Jolokia,不适用于WebFlux)。需要引入依赖jolokia-core。 |
logfile |
返回日志文件的内容(如果已设置logging.file.name或logging.file.path属性)。支持使用HTTPRange标头来检索部分日志文件的内容。 |
prometheus |
以Prometheus服务器可以抓取的格式公开指标。需要依赖micrometer-registry-prometheus。 |
其中最常用的Endpoint:
- Health:监控状况
- Metrics:运行时指标
- Loggers:日志记录
Health Endpoint
健康检查端点,我们一般用于在云平台,平台会定时的检查应用的健康状况,我们就需要Health Endpoint可以为平台返回当前应用的一系列组件健康状况的集合。
重要的几点:
- health endpoint返回的结果,应该是一系列健康检查后的一个汇总报告。
- 很多的健康检查默认已经自动配置好了,比如:数据库、redis等。
- 可以很容易的添加自定义的健康检查机制。
Metrics Endpoint
提供详细的、层级的、空间指标信息,这些信息可以被pull(主动推送)或者push(被动获取)方式得到:
- 通过Metrics对接多种监控系统。
- 简化核心Metrics开发。
- 添加自定义Metrics或者扩展已有Metrics。
开启与禁用Endpoints
- 默认所有的Endpoint除过shutdown都是开启的。
- 需要开启或者禁用某个Endpoint。配置模式为
management.endpoint.<endpointName>.enabled = true
1 | management: |
- 或者禁用所有的Endpoint然后手动开启指定的Endpoint。
1 | management: |
暴露Endpoints
支持的暴露方式
- HTTP:默认只暴露health和info。
- JMX:默认暴露所有Endpoint。
- 除过health和info,剩下的Endpoint都应该进行保护访问。如果引入Spring Security,则会默认配置安全访问规则。
| ID | JMX | Web |
|---|---|---|
auditevents |
Yes | No |
beans |
Yes | No |
caches |
Yes | No |
conditions |
Yes | No |
configprops |
Yes | No |
env |
Yes | No |
flyway |
Yes | No |
health |
Yes | Yes |
heapdump |
N/A | No |
httptrace |
Yes | No |
info |
Yes | Yes |
integrationgraph |
Yes | No |
jolokia |
N/A | No |
logfile |
N/A | No |
loggers |
Yes | No |
liquibase |
Yes | No |
metrics |
Yes | No |
mappings |
Yes | No |
prometheus |
N/A | No |
scheduledtasks |
Yes | No |
sessions |
Yes | No |
shutdown |
Yes | No |
startup |
Yes | No |
threaddump |
Yes | No |
若要更改公开的Endpoint,请配置以下的包含和排除属性:
| Property | Default |
|---|---|
management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.exclude |
|
management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.include |
* |
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude |
|
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include |
info, health |
3.定制Endpoint
定制 Health 信息
1 | management: |
通过实现HealthIndicator接口,或继承MyComHealthIndicator类。
1 | import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health; |
定制info信息
常用两种方式:
- 编写配置文件
1 | info: |
- 编写InfoContributor
1 | import java.util.Collections; |
http://localhost:8080/actuator/info 会输出以上方式返回的所有info信息
定制Metrics信息
增加定制Metrics:
1 | class MyService{ |
定制Endpoint
1 | @Component |
场景:
- 开发ReadinessEndpoint来管理程序是否就绪。
- 开发LivenessEndpoint来管理程序是否存活。
4.Boot Admin Server
可视化指标监控
- 把前面的json数据用前端页面包含一下, 提高可读性
What is Spring Boot Admin?
codecentric’s Spring Boot Admin is a community project to manage and monitor your Spring Boot ® applications. The applications register with our Spring Boot Admin Client (via HTTP) or are discovered using Spring Cloud ® (e.g. Eureka, Consul). The UI is just a Vue.js application on top of the Spring Boot Actuator endpoints.
9、springboot高级特性
1.Profile环境切换
为了方便多环境适配,Spring Boot简化了profile功能。
1 | 1. 默认配置文件application.yaml任何时候都会加载。 |
@Profile条件装配功能
Person.java
1 | @Data |
application.properties
1 | person: |
application-test.yaml
1 | person: |
application-prod.yaml
1 | person: |
application.properties
1 | # 激活prod配置文件 |
@Profile还可以修饰在方法上:
1 | class Color { |
可以激活一组:
1 | spring.profiles.active=production |
2.配置加载优先级
外部化配置
官方文档 - Externalized Configuration
Spring Boot uses a very particular PropertySource order that is designed to allow sensible overriding of values. Properties are considered in the following order (with values from lower items overriding earlier ones)(1优先级最低,14优先级最高):
- Default properties (specified by setting
SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties). @PropertySourceannotations on your@Configurationclasses. Please note that such property sources are not added to theEnvironmentuntil the application context is being refreshed. This is too late to configure certain properties such aslogging.*andspring.main.*which are read before refresh begins.- Config data (such as
application.propertiesfiles) - A
RandomValuePropertySourcethat has properties only inrandom.*. - OS environment variables.
- Java System properties (
System.getProperties()). - JNDI attributes from
java:comp/env. ServletContextinit parameters.ServletConfiginit parameters.- Properties from
SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON(inline JSON embedded in an environment variable or system property). - Command line arguments.
propertiesattribute on your tests. Available on@SpringBootTestand the test annotations for testing a particular slice of your application.@TestPropertySourceannotations on your tests.- Devtools global settings properties in the
$HOME/.config/spring-bootdirectory when devtools is active.
1 | import org.springframework.stereotype.*; |
-
外部配置源
- Java属性文件。
- YAML文件。
- 环境变量。
- 命令行参数。
-
配置文件查找位置
- classpath 根路径。
- classpath 根路径下config目录。
- jar包当前目录。
- jar包当前目录的config目录。
- /config子目录的直接子目录。
-
配置文件加载顺序:
1
2
3
41. 当前jar包内部的application.properties和application.yml。
2. 当前jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties 和 application-{profile}.yml。
3. 引用的外部jar包的application.properties和application.yml。
4. 引用的外部jar包的application-{profile}.properties和application-{profile}.yml -
指定环境优先,外部优先,后面的可以覆盖前面的同名配置项。
3.自定义starter细节
starter启动原理
- starter的pom.xml引入autoconfigure依赖
1 | graph LR |
- autoconfigure包中配置使用
META-INF/spring.factories中EnableAutoConfiguration的值,使得项目启动加载指定的自动配置类 - 编写自动配置类
xxxAutoConfiguration->xxxxProperties -
@Configuration@Conditional@EnableConfigurationProperties@Bean- …
- 引入starter —
xxxAutoConfiguration— 容器中放入组件 ----绑定xxxProperties---- 配置项
自定义starter
- 目标:创建
HelloService的自定义starter。 - 创建两个工程,分别命名为
hello-spring-boot-starter(普通Maven工程),hello-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure(需用用到Spring Initializr创建的Maven工程)。 hello-spring-boot-starter无需编写什么代码,只需让该工程引入hello-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure依赖:
1 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
hello-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure的pom.xml如下:
1 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
- 创建4个文件:
com/lun/hello/auto/HelloServiceAutoConfigurationcom/lun/hello/bean/HelloPropertiescom/lun/hello/service/HelloServicesrc/main/resources/META-INF/spring.factories
1 | import com.lun.hello.bean.HelloProperties; |
- 用maven插件,将两工程install到本地。
- 接下来,测试使用自定义starter,用Spring Initializr创建名为
hello-spring-boot-starter-test工程,引入hello-spring-boot-starter依赖,其pom.xml如下:
1 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
- 添加配置文件
application.properties:
1 | hello.prefix=hello |
- 添加单元测试类:
1 | import com.lun.hello.service.HelloService;//来自自定义starter |
4.⭐️SpringApplication创建初始化流程
1.SpringBoot启动过程
Spring Boot应用的启动类:
1 | import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; |
spring.factories:
1 | ... |
2.SpringBoot完整启动过程
继续上一节,接着讨论return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args)的run方法
1 | public class SpringApplication { |
5.自定义事件监听组件
1 | MyApplicationContextInitializer.java |
注册MyApplicationContextInitializer,MyApplicationListener,MySpringApplicationRunListener:
resources / META-INF / spring.factories:
1 | org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ |
🔯LAST
路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索。
- Spring Boot 2 场景整合篇
- 虚拟化技术
- 安全控制
- 缓存技术
- 消息中间件
- 对象存储
- 定时调度
- 异步任务
- 分布式系统
- Spring Boot 2 响应式编程
- 响应式编程基础
- Webflux开发Web应用
- 响应式访问持久化层
- 响应式安全开发
- 响应式原理