02springboot自动配置&配置文件
三、自动配置
13、自动配置【源码分析】-自动包规则原理
Spring Boot应用的启动类:
1 | @SpringBootApplication |
分析下@SpringBootApplication
1 | @Target(ElementType.TYPE) |
重点分析
@SpringBootConfiguration@EnableAutoConfiguration@ComponentScan
@SpringBootConfiguration
1 | @Target(ElementType.TYPE) |
@Configuration代表当前是一个配置类。
@ComponentScan
指定扫描哪些Spring注解。
@ComponentScan 在07、基础入门-SpringBoot-自动配置特性有用例。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
- 是
@AutoConfigurationPackage以及
1 | // |
重点分析@AutoConfigurationPackage,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)。
@AutoConfigurationPackage
标签名直译为:自动配置包,指定了默认的包规则。
- 将指定的一个包下的所有组件导入进来
- MainApplication程序所在的包下的组件
1 | @Target(ElementType.TYPE) |
- 利用Registrar给容器中导入一系列组件
- 将指定的一个包下的所有组件导入进MainApplication所在包下。
14、自动配置【源码分析】-初始加载自动配置类
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
-
利用
getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件 -
调用
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取到所有需要导入到容器中的配置类 -
利用工厂加载
Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader);得到所有的组件 -
从
1
META-INF/spring.factories
位置来加载一个文件。
- 默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有
META-INF/spring.factories位置的文件 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面也有META-INF/spring.factories
- 默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有

1 | # 文件里面写死了spring-boot一启动就要给容器中加载的所有配置类 |
虽然我们127个场景的所有自动配置启动的时候默认全部加载,但是xxxxAutoConfiguration按照条件装配规则(@Conditional),最终会按需配置。
如AopAutoConfiguration类:
1 | @Configuration( |
15、自动配置【源码分析】-自动配置流程
以DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration的内部类DispatcherServletConfiguration为例子:
1 | @Bean |
- SpringBoot默认会在底层配好所有的组件,但是如果用户自己配置了以用户的优先。
总结:
- SpringBoot先加载所有的自动配置类
xxxxxAutoConfiguration - 每个自动配置类按照条件进行生效,默认都会绑定配置文件指定的值。(
xxxxProperties里面读取,xxxProperties和配置文件进行了绑定) - 生效的配置类就会给容器中装配很多组件
- 只要容器中有这些组件,相当于这些功能就有了
- 定制化配置
- 用户直接自己@Bean替换底层的组件
- 用户去看这个组件是获取的配置文件什么值就去修改。(修改配置文件
application.properties)
xxxxxAutoConfiguration —> 组件 —> xxxxProperties里面拿值 ----> application.properties
16、最佳实践-SpringBoot应用如何编写
-
引入场景依赖
-
查看自动配置了哪些(选做)
-
自己分析,引入场景对应的自动配置一般都生效了
-
配置文件中
1
debug=true
开启自动配置报告。
Negative(不生效) : 消极的Positive(生效) : 积极的
-
-
是否需要修改
-
参照文档修改配置项
- springboot官方文档
- 自己分析。xxxxProperties绑定了配置文件的哪些。
比如
spring.banner.image.location1
2spring.banner.image.location=classpath:picture.png
# 默认是 resource 目录下的banner.gif (jpg or png can also be used) -
自定义加入或者替换组件
- @Bean、@Component…
-
自定义器 XXXXXCustomizer;
-
…
-
17、最佳实践-Lombok简化开发
Lombok用标签方式代替构造器、getter/setter、toString()等冗余代码
spring boot已经管理Lombok。
- 引入依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
IDEA中File->Settings->Plugins,搜索安装Lombok插件。
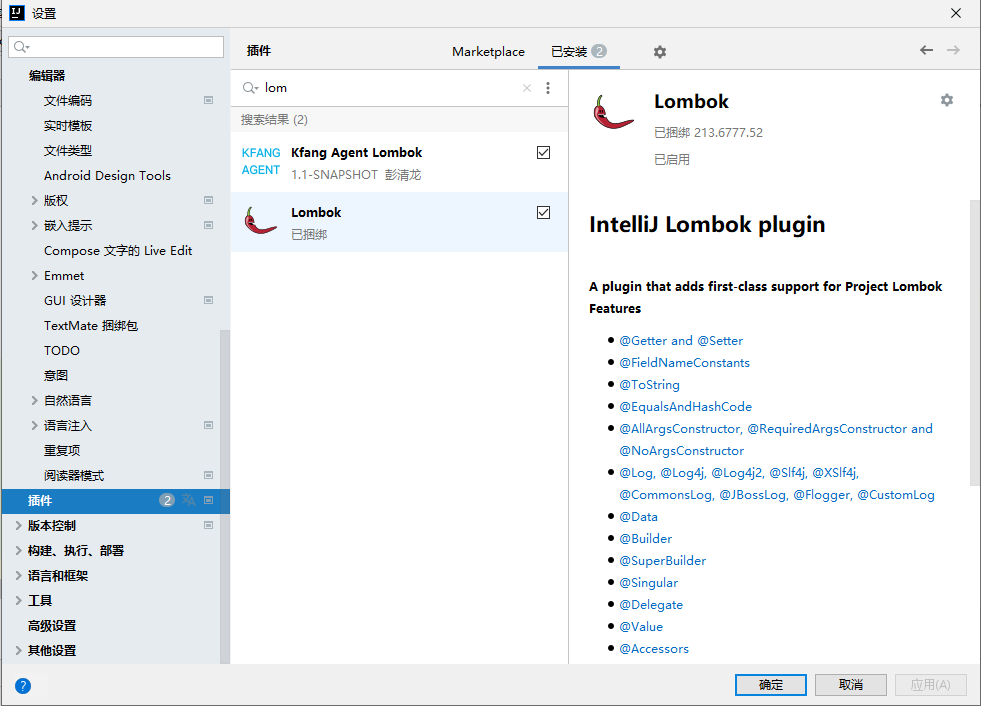
会在编译的时候自动加上相应的方法, 而不会添加在源代码上
常用注解
@Setter注解在类或字段,注解在类时为所有字段生成setter方法,注解在字段上时只为该字段生成setter方法。@Getter使用方法同上,区别在于生成的是getter方法。@ToString注解在类,添加toString方法。@EqualsAndHashCode注解在类,生成hashCode和equals方法。@NoArgsConstructor注解在类,生成无参的构造方法。@RequiredArgsConstructor注解在类,为类中需要特殊处理的字段生成构造方法,比如final和被@NonNull注解的字段。@AllArgsConstructor注解在类,生成包含类中全参构造器。@Data注解在类,生成setter/getter、equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString方法,如为final属性,则不会为该属性生成setter方法。@Slf4j注解在类,生成log变量,严格意义来说是常量。private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class);
如果需要部分参数的构造器, 就需要自己写
1 | @NoArgsConstructor |
简化日志开发
1 | @Slf4j |
Lombok的优缺点
- 优点:
- 能通过注解的形式自动生成构造器、getter/setter、equals、hashcode、toString等方法,提高了一定的开发效率
- 让代码变得简洁,不用过多的去关注相应的方法
- 属性做修改时,也简化了维护为这些属性所生成的getter/setter方法等
- 缺点:
- 不支持多种参数构造器的重载
- 虽然省去了手动创建getter/setter方法的麻烦,但大大降低了源代码的可读性和完整性,降低了阅读源代码的舒适度
18、最佳实践-dev-tools
- 实际上还是重启(
Automatic Restart)- 如果想要使用热更新(
Reload), 需要使用到JRebel(付费的)
- 如果想要使用热更新(
spring-boot-devtools模块可以包含在任何项目中,它可以节省大量的时间。 想要使用devtools支持,只需将模块依赖关系添加到你的构建中
spring-boot-devtools会在类路径上的文件发生更改时自动重启。
Spring Boot includes an additional set of tools that can make the application development experience a little more pleasant. The
spring-boot-devtoolsmodule can be included in any project to provide additional development-time features.——linkApplications that use
spring-boot-devtoolsautomatically restart whenever files on the classpath change. This can be a useful feature when working in an IDE, as it gives a very fast feedback loop for code changes. By default, any entry on the classpath that points to a directory is monitored for changes. Note that certain resources, such as static assets and view templates, do not need to restart the application.——linkTriggering a restart
As DevTools monitors classpath resources, the only way to trigger a restart is to update the classpath. The way in which you cause the classpath to be updated depends on the IDE that you are using:
- In Eclipse, saving a modified file causes the classpath to be updated and triggers a restart.
- In IntelliJ IDEA, building the project (
Build -> Build Project)(shortcut: Ctrl+F9) has the same effect.
添加依赖:
1 | <dependencies> |
在IDEA中,项目或者页面修改以后:Ctrl+F9(重新编译)。
19、最佳实践-Spring Initailizr(项目初始化向导)
- Spring Initializr 从本质上来说就是一个Web应用程序,它能生成Spring Boot项目结构。虽然不能生成应用程序代码,但可以提供一个基本的项目结构,以及一个用于构建代码的Maven或Gradle构建说明文件。只需要写应用程序的代码就好了。
Spring Initailizr是创建Spring Boot工程向导。
在IDEA中,菜单栏New -> Project -> Spring Initailizr。
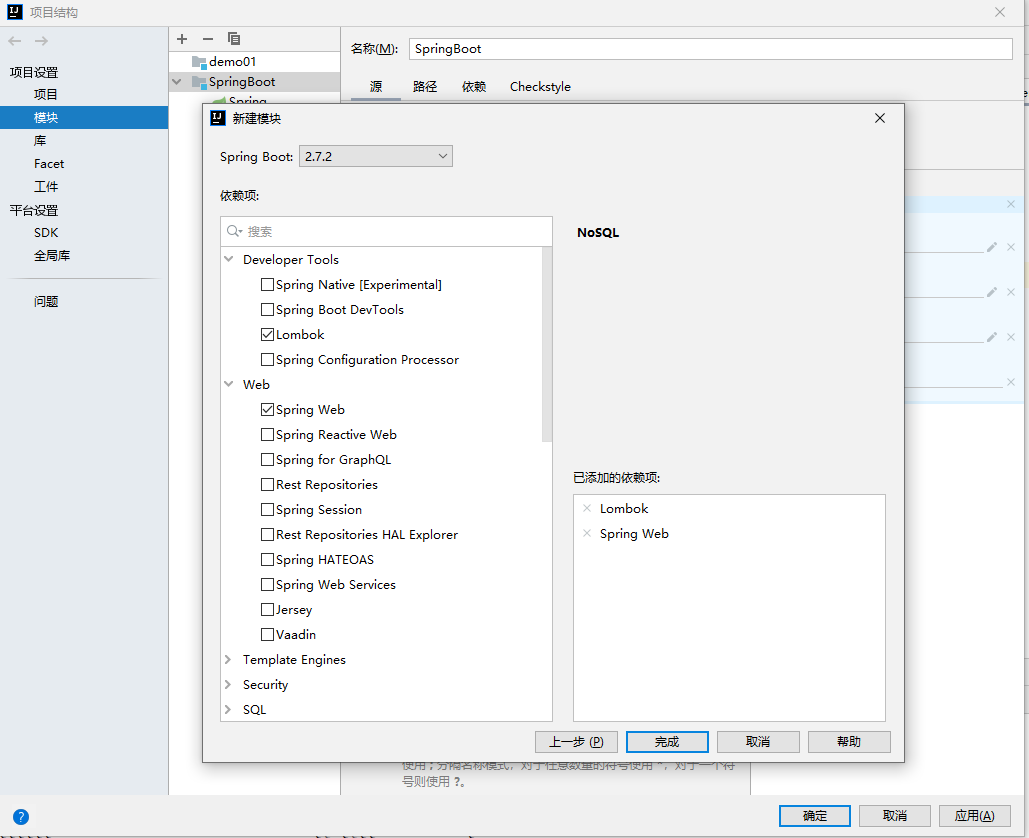
四、配置文件
20、配置文件-yaml的用法
- 同以前的properties用法
YAML 是 “YAML Ain’t Markup Language”(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。
在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)。
非常适合用来做以数据为中心的配置文件。
基本语法
- key: value;kv之间有空格
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
- '#'表示注释
- 字符串无需加引号,如果要加,单引号’’、双引号""表示字符串内容会被 转义、不转义
数据类型
- 字面量:单个的、不可再分的值。date、boolean、string、number、null
1 | k: v |
- 对象:键值对的集合。map、hash、set、object
1 | #行内写法: |
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值。array、list、queue
1 | #行内写法: |
实例
1 | @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") |
用yaml表示以上对象
- 对于普通的字符串, 不需要使用引号
- 如果使用单引号 ’ ’ , 就是普通的字符串, 即使有转义字符 , 也会将转义字符作为字符串直接输出 :
张三\n李四--> 张三\n李四 - 如果使用双引号 " ", 如果有转移字符, 转义字符就会正常的起作用 :
\n --> 张三 李四 **application.yml**```yamlperson: userName: dhx_ boss: true birth: 2019/12/21 age: 18 #interests: [吃饭,睡觉,玩游戏] interests: - 篮球 - 睡觉 - 吃饭 - 玩游戏 animal: [cat,dog,fish]# score:# english: 10# math: 90 score: {english:80,math:90} salarys: - 9999.1 - 999.2 pet: name: Tom weight: 10 allPets: sick: - {name:阿狗,weight:90.1} - name: 阿猫 weight: 88.66 - name: 阿蛇 weight: 77.77 health: - {name:大狗,weight:90.1} - name: 大猫 weight: 88.66 - name: 大蛇 weight: 77.77
controller:
1 | @RestController |
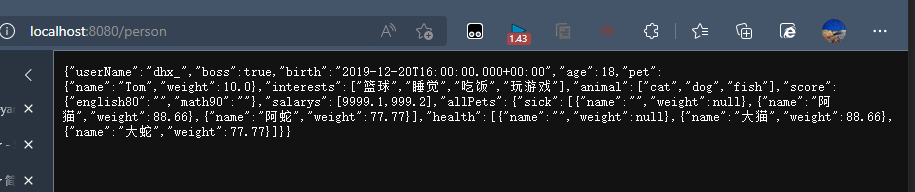
1 | {"userName":"dhx_","boss":true,"birth":"2019-12-20T16:00:00.000+00:00","age":18,"pet":{"name":"Tom","weight":10.0},"interests":["篮球","睡觉","吃饭","玩游戏"],"animal":["cat","dog","fish"],"score":{"english80":"","math90":""},"salarys":[9999.1,999.2],"allPets":{"sick":[{"name":"","weight":null},{"name":"阿猫","weight":88.66},{"name":"阿蛇","weight":77.77}],"health":[{"name":"","weight":null},{"name":"大猫","weight":88.66},{"name":"大蛇","weight":77.77}]}} |
当同时存在application.properties以及application.yml文件时, 会以properties的内容优先

21、配置文件-自定义类绑定的配置提示
You can easily generate your own configuration metadata file from items annotated with
@ConfigurationPropertiesby using thespring-boot-configuration-processorjar. The jar includes a Java annotation processor which is invoked as your project is compiled.——link
自定义的类和配置文件绑定一般没有提示。若要提示,添加如下依赖:
1 | <dependency> |