粘包&半包
粘包(Packet Concatenation) : 粘包指的是发送方发送的多个小数据包在传输过程中被接收方合并成一个大数据包的现象 。这种情况下,接收方无法准确地将大数据包拆分成原来的小数据包,导致数据粘连。粘包问题常见于使用面向流的传输协议(如TCP)进行数据传输时,由于TCP协议以字节流的形式传输数据,不保留数据包边界信息。
半包(Incomplete Packet) : 半包指的是接收方在读取数据时,并没有完整地接收到一个完整的数据包,而只接收到了部分数据包或者不完整的数据包 。这可能发生在接收缓冲区的数据还未达到一个完整数据包的长度时,接收方就开始读取数据,从而造成数据包的不完整。
粘包
server
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldServer.class);void start () { NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup (1 ); NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup (); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap (); serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class); serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker); serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { log.debug("connected {}" , ctx.channel()); super .channelActive(ctx); } @Override public void channelInactive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { log.debug("disconnect {}" , ctx.channel()); super .channelInactive(ctx); } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080 ); log.debug("{} binding..." , channelFuture.channel()); channelFuture.sync(); log.debug("{} bound..." , channelFuture.channel()); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("server error" , e); } finally { boss.shutdownGracefully(); worker.shutdownGracefully(); log.debug("stopped" ); } } public static void main (String[] args) { new HelloWorldServer ().start(); }
client
客户端代码希望发送 10 个消息,每个消息是 16 字节
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldClient.class);public static void main (String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup (); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap (); bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); bootstrap.group(worker); bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { log.debug("connected..." ); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { log.debug("sending..." ); Random r = new Random (); char c = 'a' ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(); buffer.writeBytes(new byte []{0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 }); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1" , 8080 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("client error" , e); } finally { worker.shutdownGracefully(); } }
服务器端的某次输出,可以看到一次就接收了 160 个字节,而非分 10 次接收
半包
客户端代码希望发送 1 个消息,这个消息是 160 字节,代码改为
1 2 3 4 5 ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { buffer.writeBytes(new byte []{0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 }); } ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
为现象明显,服务端修改一下接收缓冲区,其它代码不变
1 serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10 );
服务器端的某次输出,可以看到接收的消息被分为多个字节 , 分别是 36 40 40 40 4 B
注意
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10) 影响的底层接收缓冲区(即滑动窗口)大小,仅决定了 netty 读取的最小单位 ,netty 实际每次读取的一般是它的整数倍
分析
粘包
现象,发送 abc def,接收 abcdef
原因
应用层:接收方 ByteBuf 设置太大(Netty 默认 1024)
滑动窗口:假设发送方 256 bytes 表示一个完整报文,但由于接收方处理不及时且窗口大小足够大,这 256 bytes 字节就会缓冲在接收方的滑动窗口中,当滑动窗口中缓冲了多个报文就会粘包
Nagle 算法:会造成粘包
半包
现象,发送 abcdef,接收 abc def
原因
应用层:接收方 ByteBuf 小于实际发送数据量
滑动窗口:假设接收方的窗口只剩了 128 bytes,发送方的报文大小是 256 bytes,这时放不下了,只能先发送前 128 bytes,等待 ack 后才能发送剩余部分,这就造成了半包
MSS 限制:当发送的数据超过 MSS 限制后,会将数据切分发送,就会造成半包
本质是因为 TCP 是流式协议,消息无边界
更多TCP有关知识 , 参考传输层-计算机网络| dhx_'blog
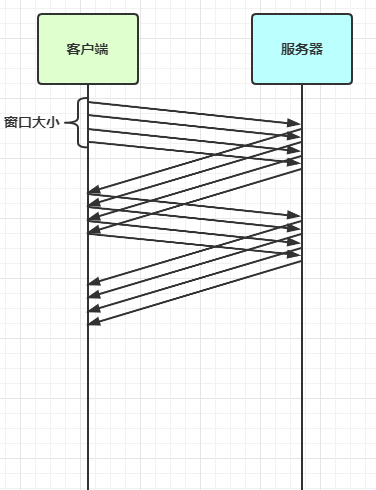
滑动窗口
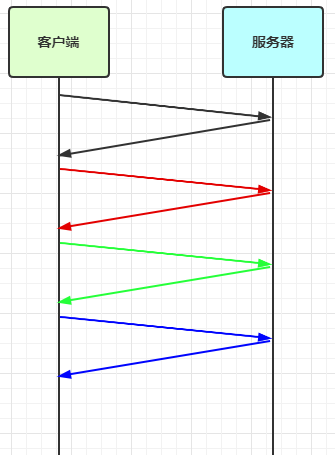
TCP 以一个段(segment)为单位,每发送一个段就需要进行一次确认应答(ack)处理,但如果这么做,缺点是包的往返时间越长性能就越差
为了解决此问题,引入了窗口概念,窗口大小即决定了无需等待应答而可以继续发送的数据最大值
窗口实际就起到一个缓冲区的作用,同时也能起到流量控制的作用
图中深色的部分即要发送的数据,高亮的部分即窗口
窗口内的数据才允许被发送,当应答未到达前,窗口必须停止滑动
如果 1001~2000 这个段的数据 ack 回来了,窗口就可以向前滑动
接收方也会维护一个窗口,只有落在窗口内的数据才能允许接收
MSS
Maximum Segment Size ,最大报文长度,TCP payload的最大值,TCP协议定义的一个选项,MSS是TCP用来限制应用层最大的发送字节数 , MSS 是最大段长度(maximum segment size),它是 MTU 刨去 tcp 头和 ip 头后剩余能够作为数据传输的字节数
链路层对一次能够发送的最大数据有限制,这个限制称之为 MTU(maximum transmission unit),不同的链路设备的 MTU 值也有所不同,例如
以太网的 MTU 是 1500 FDDI(光纤分布式数据接口)的 MTU 是 4352 本地回环地址的 MTU 是 65535 - 本地测试不走网卡 ipv4 tcp 头占用 20 bytes,ip 头占用 20 bytes,因此以太网 MSS 的值为 1500 - 40 = 1460
TCP 在传递大量数据时,会按照 MSS 大小将数据进行分割发送
MSS 的值在三次握手时通知对方自己 MSS 的值,然后在两者之间选择一个小值作为 MSS
Nagle 算法
即使发送一个字节,也需要加入 tcp 头和 ip 头,也就是总字节数会使用 41 bytes,对于拥挤的网络资源来说显然是不合理的。因此为了提高网络利用率,tcp 希望尽可能发送足够大的数据,这就是 Nagle 算法产生的缘由
该算法是指发送端即使还有应该发送的数据,但如果这部分数据很少的话,则进行延迟发送
如果 SO_SNDBUF 的数据达到 MSS,则需要发送
如果 SO_SNDBUF 中含有 FIN(表示需要连接关闭)这时将剩余数据发送,再关闭
如果 TCP_NODELAY = true,则需要发送
已发送的数据都收到 ack 时,则需要发送
上述条件不满足,但发生超时(一般为 200ms)则需要发送
除上述情况,延迟发送
Nagle算法要求,一个TCP连接在任意时刻,最多只能有一个没有被确认的小段。所谓“小段”指的是小于MSS的数据块,“没有被确认”指的是一个数据块发送出去后,没有收到对方发送的ACK确认该数据已收到。
Nagle算法的实现规则:
如果包长度达到MSS,则允许发送;
如果该包含有FIN,则允许发送;
设置了TCP_NODELAY选项,则允许发送;
未设置TCP_CORK选项时,若所有发出去的小数据包(包长度小于MSS)均被确认,则允许发送;
上述条件都未满足,但发生了超时(一般为200ms),则立即发送。
解决
短链接,发一个包建立一次连接 ,这样连接建立到连接断开之间就是消息的边界,缺点效率太低
每一条消息采用固定长度,缺点浪费空间
每一条消息采用分隔符,例如 \n,缺点需要转义
每一条消息分为 head 和 body,head 中包含 body 的长度
短链接
客户端与服务器建立连接后进行一次或多次数据交换,然后立即关闭连接的方式。
简单来说,当数据交换完成后,连接就会被关闭 。这种连接方式具有开销较小、资源消耗少 的优点。但是,由于每次通信都需要重新建立连接,对于频繁通信的应用来说,建立和断开连接的开销可能会导致性能下降 。
只需要更改client代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldClient.class);public static void main (String[] args) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { send(); } } private static void send () { NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup (); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap (); bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); bootstrap.group(worker); bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { log.debug("conneted..." ); ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { log.debug("sending..." ); ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(); buffer.writeBytes(new byte []{0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 }); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); ctx.close(); } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost" , 8080 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("client error" , e); } finally { worker.shutdownGracefully(); } }
输出,略
半包用这种办法还是不好解决,因为接收方的缓冲区大小是有限的
固定长度
让所有数据包长度固定(假设长度为 10 字节) ,服务器端代码加入
服务端的代码需要添加一个FixedLengthFrameDecoder解码器
客户端测试代码
注意, 采用这种方法后,客户端什么时候 flush 都可以
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldClient.class);public static void main (String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup (); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap (); bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); bootstrap.group(worker); bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { log.debug("connected..." ); ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { log.debug("sending..." ); Random r = new Random (); char c = 'a' ; ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { byte [] bytes = new byte [10 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j < r.nextInt(10 ); j++) { bytes[j] = (byte ) c; } c++; buffer.writeBytes(bytes); } ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost" , 8080 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("client error" , e); } finally { worker.shutdownGracefully(); } }
缺点是,数据包的大小不好把握
长度定的太大,浪费
长度定的太小,对某些数据包又显得不够
固定分隔符
服务端加入,默认以 \n 或 \r\n 作为分隔符,如果超出指定长度仍未出现分隔符,则抛出异常
1 2 ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder (1024 ));
客户端在每条消息之后,加入 \n 分隔符
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class LineBasedClient { static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldClient.class); public static void main (String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup (); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap (); bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); bootstrap.group(worker); bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { log.debug("connected..." ); ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { log.debug("sending..." ); Random r = new Random (); char c = 'a' ; ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= r.nextInt(16 )+1 ; j++) { buffer.writeByte((byte ) c); } buffer.writeByte(10 ); c++; } ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost" , 8080 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("client error" , e); } finally { worker.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
缺点,处理字符数据比较合适,但如果内容本身包含了分隔符(字节数据常常会有此情况),那么就会解析错误
预设长度
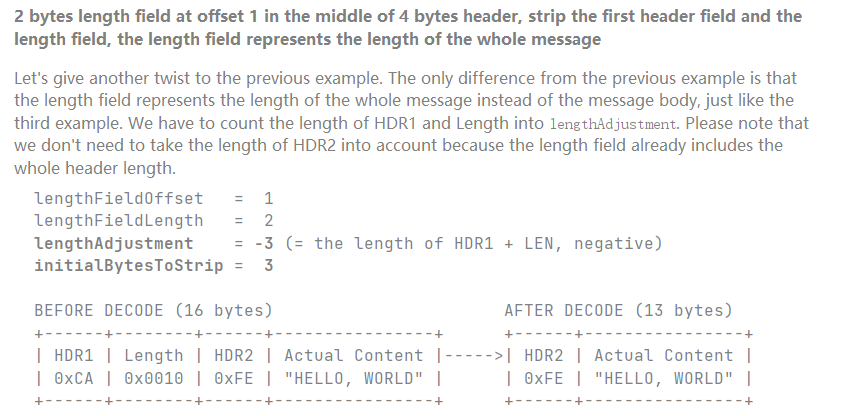
io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
lengthFieldoffset 长度字段偏移量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder ( int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength, int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip) { this ( maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength, lengthAdjustment, initialBytesToStrip, true ); }
测试代码:
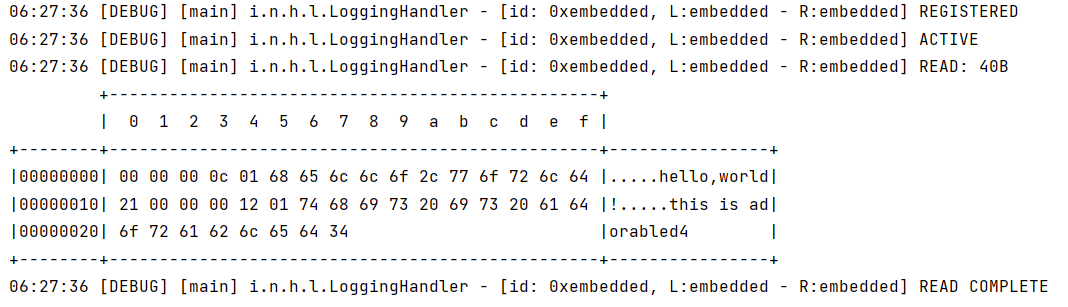
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class TestLengthFieldDecoder { public static void main (String[] args) { EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel ( new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG), new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder (1024 ,0 ,4 ,1 ,4 ) ); ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(); send(buffer,"hello,world!" ); send(buffer,"this is adorabled4" ); channel.writeInbound(buffer); } private static void send (ByteBuf buf, String msg) { byte [] bytes = msg.getBytes(); int len = bytes.length ; buf.writeInt(len); buf.writeByte(1 ); buf.writeBytes(bytes); } }
协议设计与解析
why
实现互联网通信 :网络协议是互联网通信的基础,它定义了数据在网络中传输的格式、规则和行为。通过解析和设计网络协议,可以确保不同设备和系统之间能够相互通信,并实现可靠的数据传输。提供标准化和互操作性 :网络协议的解析与设计可以制定一套通用的规范和标准,使得不同厂商和开发者能够遵循相同的规则进行开发。这样一来,不同的设备和系统就能够实现互操作性,无论其硬件、软件或操作系统的差异。优化网络性能 :通过对网络协议进行解析与设计,可以优化网络的性能和效率。例如,设计高效的路由协议可以帮助数据包快速准确地传输到目标节点,减少延迟和丢包。此外,网络协议的设计还可以考虑安全性、可扩展性和容错性等方面,进一步提高网络的性能和稳定性。支持新技术和应用的发展 :随着科技的不断进步,新的应用和技术层出不穷。解析与设计网络协议可以满足这些新技术和应用的需求,确保其能够在网络中正常运行。例如,随着物联网和5G技术的发展,对于低延迟、大规模连接和安全性的要求提高了,需要相应的网络协议来支持这些需求。
网络协议的解析与设计是构建可靠、高效和安全计算机网络的关键步骤。它不仅提供了通信的基础规范,还支持各种新技术和应用的发展,推动了互联网的进步和创新。
TCP/IP 中消息传输基于流的方式,没有边界。
协议的目的就是划定消息的边界,制定通信双方要共同遵守的通信规则
例如:在网络上传输
是中文一句著名的无标点符号句子,在没有标点符号情况下,这句话有数种拆解方式,而意思却是完全不同,所以常被用作讲述标点符号的重要性
一种解读
另一种解读
如何设计协议呢?其实就是给网络传输的信息加上“标点符号”。但通过分隔符来断句不是很好,因为分隔符本身如果用于传输,那么必须加以区分。因此,下面一种协议较为常用
例如,假设一个中文字符长度为 3,按照上述协议的规则,发送信息方式如下,就不会被接收方弄错意思了
很久很久以前,一位私塾先生到一家任教。双方签订了一纸协议:“无鸡鸭亦可无鱼肉亦可白菜豆腐不可少不得束修金”。此后,私塾先生虽然认真教课,但主人家则总是给私塾先生以白菜豆腐为菜,丝毫未见鸡鸭鱼肉的款待。私塾先生先是很不解,可是后来也就想通了:主人把鸡鸭鱼肉的钱都会换为束修金的,也罢。至此双方相安无事。
年关将至,一个学年段亦告结束。私塾先生临行时,也不见主人家为他交付束修金,遂与主家理论。然主家亦振振有词:“有协议为证——无鸡鸭亦可,无鱼肉亦可,白菜豆腐不可少,不得束修金。这白纸黑字明摆着的,你有什么要说的呢?”
私塾先生据理力争:“协议是这样的——无鸡,鸭亦可;无鱼,肉亦可;白菜豆腐不可,少不得束修金。”
双方唇枪舌战,你来我往,真个是不亦乐乎!
这里的束修金,也作“束脩”,应当是泛指教师应当得到的报酬
协议数据单元 PDU(Protocol Data Unit)是指对等层次之间传递的数据单位。协议数据单元 (Protocol Data Unit )物理层的 PDU是数据位 (bit),数据链路层 的 PDU是数据帧 (frame ),网络层 的PDU是数据包(packet),传输层 的 PDU是数据段 (segment),其他更高层次的PDU是数据(data)。
RESP协议
Redis客户端使用RESP(Redis的序列化协议)协议与Redis的服务器端进行通信。 虽然该协议是专门为Redis设计的,但是该协议也可以用于其他 客户端-服务器 (Client-Server)软件项目。
RESP协议在Redis 1.2版本中引入,但它已成为在Redis 2.0版本中与Redis服务器沟通的标准方式。这是您应该在Redis客户端中实现的协议。
RESP实际上是一个支持以下数据类型的序列化协议:简单字符串(Simple Strings),错误(Errors),整数(Integers),块字符串(Bulk Strings)和数组(Arrays)。
在Redis中,RESP用作 请求-响应 协议的方式如下:
1、客户端将命令作为批量字符串的RESP数组发送到Redis服务器。
2、服务器(Server)根据命令执行的情况返回一个具体的RESP类型作为回复。
在RESP协议中,有些的数据类型取决于第一个字节:
1、对于简单字符串,回复的第一个字节是“+”
2、对于错误,回复的第一个字节是“ - ”
3、对于整数,回复的第一个字节是“:”
4、对于批量字符串,回复的第一个字节是“$”
5、对于数组,回复的第一个字节是“*”
此外,稍后会讲RESP协议能够使用指定的 Bulk Strings 或Array 的特殊变量来表示空值。
在RESP协议中,协议的不同部分始终以“ ”(CRLF)结尾。
---- 最详细的Redis通信协议规范 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
举一个简单的例子, 对于我们常用的set key value 命令
例如 set name adorabled4
在解析之后 , 格式如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 *3 $3 SET $4 name $10 adorabled4
这个命令的实际协议值如下:
"*3\r\n$3\r\nSET\r\n$4\r\nname\r\n$10\r\nadorabled4\r\n"
只要我们满足RESP协议的要求 , 就可以直接通过客户端发送命令
注意这里的Redis Server没有设置密码
byte[] LINE = {13, 10}; 代表字符 \r\n
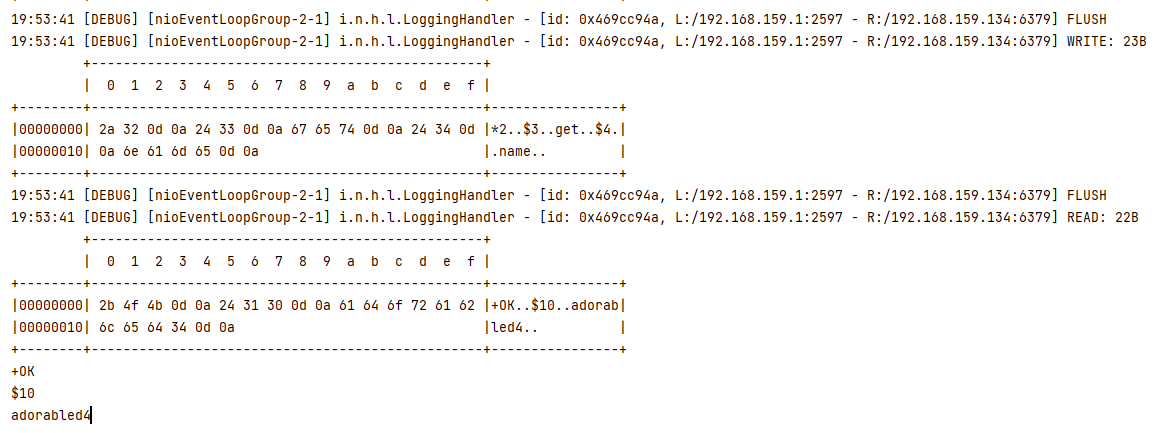
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup ();byte [] LINE = {13 , 10 };try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap (); bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); bootstrap.group(worker); bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler ()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { set(ctx); get(ctx); } private void get (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(); buf.writeBytes("*2" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("$3" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("get" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("$4" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("name" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); ctx.writeAndFlush(buf); } private void set (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(); buf.writeBytes("*3" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("$3" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("set" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("$4" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("name" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("$10" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); buf.writeBytes("adorabled4" .getBytes()); buf.writeBytes(LINE); ctx.writeAndFlush(buf); } @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset())); } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("192.168.159.134" , 6379 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("client error" , e); } finally { worker.shutdownGracefully(); }
代码测试结果如下
写入和读取都执行成功
HTTP
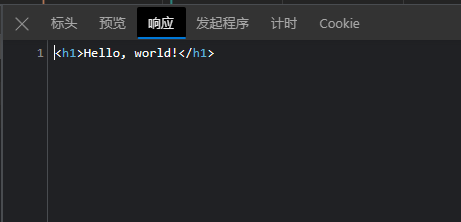
GET / HTTP/1.1musicml.net *
HTTP协议是典型的文本协议
可读性好,便于调试;
扩展性较好,能通过key:value扩展;
解析效率不高,一行一行读入,按照冒号分割,解析key和value;
对二进制不友好 ,比如语音/视频等;
Server
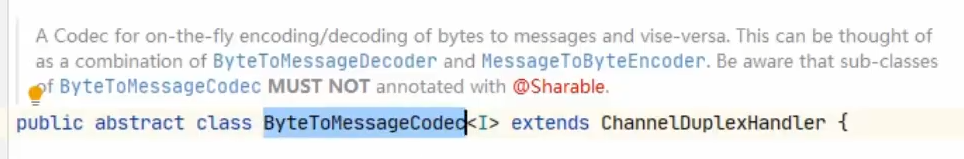
带有***Codec的类, 通常带有编码以及解码的操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 @Slf4j public class HttpClient { public static void main (String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup (); NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup (); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap (); serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class); serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker); serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec ()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler <HttpRequest>() { @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpRequest msg) throws Exception { log.debug(msg.uri()); DefaultFullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse (msg.protocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK); byte [] bytes = "<h1>Hello, world!</h1>" .getBytes(); response.headers().setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, bytes.length); response.content().writeBytes(bytes); ctx.writeAndFlush(response); } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch ( InterruptedException e) { log.error("server error" , e); } finally { boss.shutdownGracefully(); worker.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
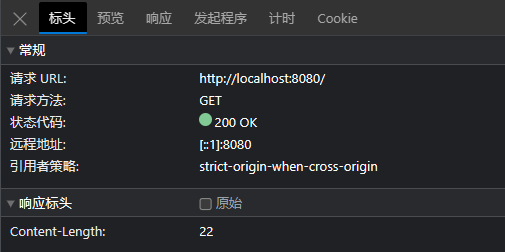
通过浏览器访问 localhost:8080 , 可以得到下面的结果
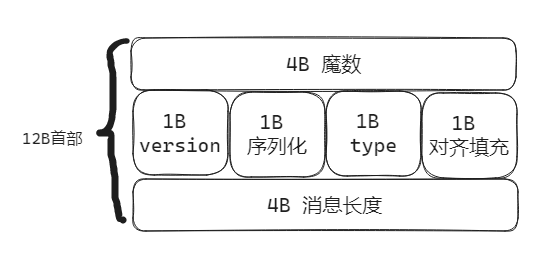
自定义协议要素
魔数,用来在第一时间判定是否是无效数据包
版本号,可以支持协议的升级
序列化算法,消息正文到底采用哪种序列化反序列化方式,可以由此扩展,例如:json、protobuf、hessian、jdk
指令类型,是登录、注册、单聊、群聊… 跟业务相关
请求序号,为了双工通信,提供异步能力
正文长度
消息正文
编解码器
根据上面的要素,设计一个登录请求消息和登录响应消息 ,并使用 Netty 完成收发
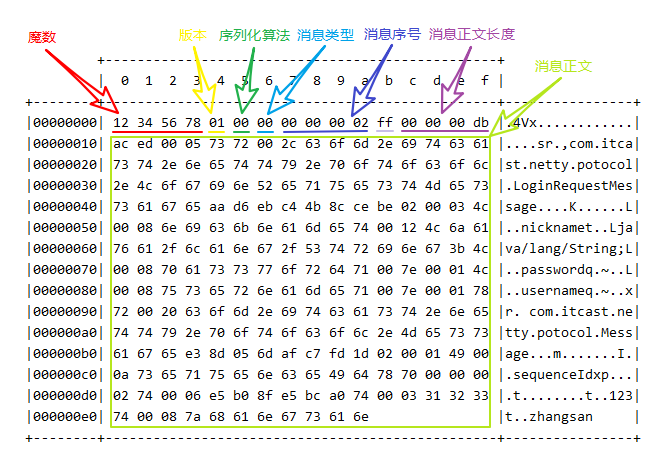
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 @Slf4j public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec <Message> { @Override protected void encode (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { out.writeBytes(new byte []{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }); out.writeByte(1 ); out.writeByte(0 ); out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType()); out.writeByte(0xff ); out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId()); ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (bos); oos.writeObject(msg); byte [] bytes = bos.toByteArray(); out.writeInt(bytes.length); out.writeBytes(bytes); } @Override protected void decode (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { int magicNum = in.readInt(); byte version = in.readByte(); byte serializerType = in.readByte(); byte messageType = in.readByte(); int sequenceId = in.readInt(); in.readByte(); int length = in.readInt(); byte [] bytes = new byte [length]; in.readBytes(bytes, 0 , length); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (bytes)); Message message = (Message) ois.readObject(); log.debug("{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}" , magicNum, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length); log.debug("{}" , message); out.add(message); } }
测试
帧解码器:
1024最大帧长度
12 偏移量 (类似于TCP头部的作用)
4 表示长度的字节(表示实际数据的长度 , 类似于TCP头部的作用)
注意使用s1.retain();增加引用计数器的数量 , 否则在调用s2的时候 , 内存已经被释放 , 会出现异常
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel ( new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder (1024 ,12 ,4 ,0 ,0 ), new LoggingHandler (), new MessageCodec () ); PingMessage msg = new PingMessage (); ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(); new MessageCodec ().encode(null , msg, buf); ByteBuf s1 = buf.slice(0 , 80 ); ByteBuf s2 = buf.slice(80 , buf.readableBytes() - 80 ); s1.retain(); channel.writeInbound(s1); channel.writeInbound(s2); }
关于 @Sharable
什么时候可以加
当 handler 不保存状态时,就可以安全地在多线程下被共享
但要注意对于编解码器类,不能继承 ByteToMessageCodec 或 CombinedChannelDuplexHandler 父类,他们的构造方法对 @Sharable 有限制
如果能确保编解码器不会保存状态,可以继承 MessageToMessageCodec 父类
一般情况下对于解码器都是不能线程共享的
@Sharable一般与具体的功能相关, 如果不需要保存状态 , 那么就不需要@Sharable
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 @ChannelHandler .Sharablepublic class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec <ByteBuf, Message> { @Override protected void encode (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> outList) throws Exception { ByteBuf out = ctx.alloc().buffer(); out.writeBytes(new byte []{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }); out.writeByte(1 ); out.writeByte(0 ); out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType()); out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId()); out.writeByte(0xff ); ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (bos); oos.writeObject(msg); byte [] bytes = bos.toByteArray(); out.writeInt(bytes.length); out.writeBytes(bytes); } @Override protected void decode (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { int magicNum = in.readInt(); byte version = in.readByte(); byte serializerType = in.readByte(); byte messageType = in.readByte(); int sequenceId = in.readInt(); in.readByte(); int len = in.readInt(); byte [] bytes = new byte [len]; in.readBytes(bytes, 0 , len); if (serializerType == 0 ) { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (bytes)); Message msg = (Message)ois.readObject(); } } }
参考